“This whole thing is amazing. Years ago, this was not something that you would think about,” said the kidney recipient, a 44-year-old Baltimore resident who spent eight years on dialysis before undergoing the transplant procedure. The patient was discharged from UMMC on Tuesday.
Maryland faculty and researchers believe this prototype organ transport blazes a trail for the use of UAS to expand access to donated organs, improving outcomes for more people in need of organ transplants.
“This history-making flight not only represents a breakthrough from a technological point of view, but provides an exemplary demonstration of how engineering expertise and ingenuity ultimately serve human needs – in this case, the need to improve the reliability and efficiency of organ delivery to hospitals conducting transplant surgery,” said Darryll J. Pines, Ph.D., UMD, dean of the A. James Clark School of Engineering and Nariman Farvardin Professor of Aerospace Engineering. “As astonishing as this breakthrough is from a purely engineering point of view, there’s a larger purpose at stake. It’s ultimately not about the technology; it’s about enhancing human life.”
Added Joseph Scalea, MD, assistant professor of surgery at UMSOM, project lead, and one of the surgeons who performed the transplant at UMMC, “As a result of the outstanding collaboration among surgeons, engineers, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), organ procurement specialists, pilots, nurses, and, ultimately, the patient, we were able to make a pioneering breakthrough in transplantation.”
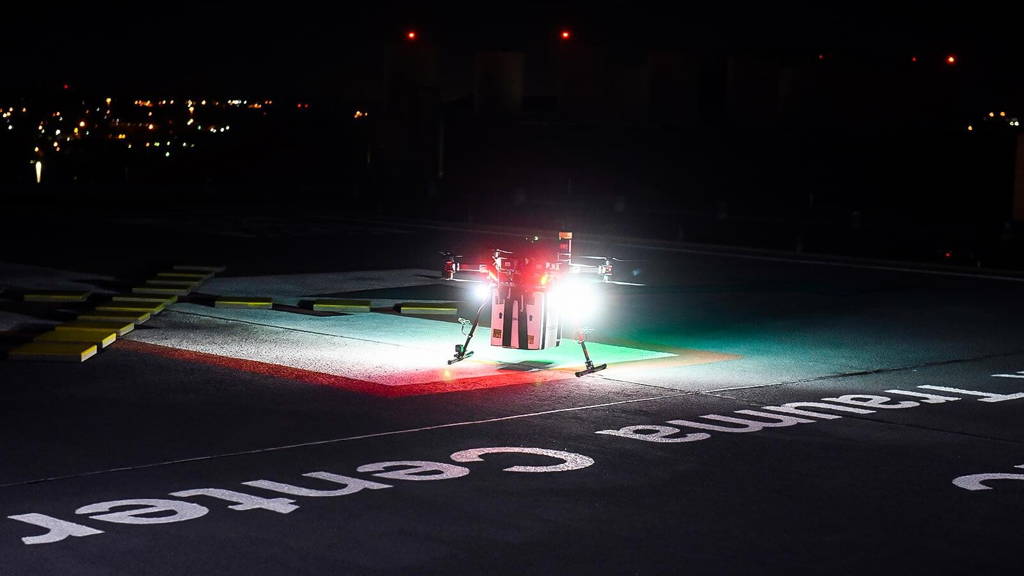
Transportation logistics are often the most complicated part of the organ transplant process.The many technological firsts of this effort include: a specially designed, high-tech apparatus for maintaining and monitoring a viable human organ; a custom-built UAS with eight rotors and multiple powertrains to ensure consistently reliable performance, even in the case of a possible component failure; the use of a wireless “mesh” network to control the UAS, monitor aircraft status, and provide communications for the ground crew at multiple locations; and aircraft operating systems that combined best practices from both UAS and organ transport standards. “We had to create a new system that was still within the regulatory structure of the FAA, but also capable of carrying the additional weight of the organ, cameras, and organ tracking, communications and safety systems over an urban, densely populated area—for a longer distance and with more endurance,” said Matthew Scassero, MPA, director of UMD’s UAS Test Site, part of the A. James Clark School of Engineering. “There’s a tremendous amount of pressure knowing there’s a person waiting for that organ, but it’s also a special privilege to be a part of this critical mission.” Prior to the April 19th organ delivery flight, the Maryland partners worked together to develop and test the UAS by first successfully transporting saline, blood tubes, and other materials, and then by transporting a healthy, but nonviable, human kidney. These test flights were preceded in 2016 by the state of Maryland’s first civil unmanned aerial delivery of simulated medical cargo, a collaborative effort between UMD’s UAS Test Site and the University of Maryland Shore Regional Health in Easton, Maryland, to illustrate how the use of UAS could radically change medical care and impact the lives of real people. Watch the first time a drone delivered a kidney to a transplant patient who had waited eight years for a donor. https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=3&v=RNYCCbCpAlM Designing a UAS Organ Delivery System To create a UAS designed to carry an organ and provide real-time monitoring of its condition, Scalea partnered with several medical technology companies to design and develop the Human Organ Monitoring and Quality Assurance Apparatus for Long-Distance Travel (HOMAL; patent pending). It measures and maintains temperature, barometric pressure, altitude, vibration, and location (via GPS) during transportation and transmits the information to the smartphones of transplant personnel. The needed unmanned aircraft and operating systems were designed by UMD UAS Test Site engineers to meet the rigid medical, technical, and regulatory demands of carrying a donor organ for human transplantation. “We built in a lot of redundancies, because we want to do everything possible to protect the payload,” said Anthony Pucciarella, director of operations at the UMD UAS Test Site. These safeguards included backup propellers and motors, dual batteries, a backup power distribution board, and a parachute recovery system (in case the entire aircraft fails). Advancing Transplantation through UAS Transport Transportation logistics are often the most complicated part of the organ transplant process –and how long an organ remains viable throughout travel is a major issue. Transport methods typically involve expensive chartered flights or rely on variable commercial flights, and occasionally result in an organ left on a plane or other delays that destroy the organ’s viability. These current transport methods also don’t adequately cover many parts of the county, such as rural or geographically remote areas, which limits access in these areas both to organ donations and organ transplants. According to the United Network for Organ Sharing, which manages the organ transplant system in the United States, in 2018 there were nearly 114,000 people on waiting lists for an organ transplant; about 1.5 percent of deceased donor organ shipments did not make it to the intended destination; and nearly four percent of organ shipments had an unanticipated delay of two or more hours. “There remains a woeful disparity between the number of recipients on the organ transplant waiting list and the total number of transplantable organs. This new technology has the potential to help widen the donor organ pool and access to transplantation,” said Scalea. “Delivering an organ from a donor to a patient is a sacred duty with many moving parts. It is critical that we find ways of doing this better.” The momentous flight was a collaboration between aviation and engineering experts at the University of Maryland’s Department of Aerospace Engineering and Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) Test Site; transplant physicians and researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) in Baltimore; and collaborators at the Living Legacy Foundation of Maryland.