A study “Understanding Clinicians’ Adoption of Mobile Health Tools: A Qualitative Review of the Most Used Frameworks” published in JMIR mHealth and uHealth proposes an aggregated technology acceptance framework that complements the gaps in existing ones and informs on the elements to look for in order to better foster mHealth adoption.
Summary:
- Although there is a push toward encouraging technology adoption in healthcare, many challenges persist.
- Researchers have been using a multitude of frameworks to help them get a better understanding of user acceptance and adoption in healthcare.
- This study looked into the frameworks used to analyze mHealth adoption in 50 peer-reviewed articles published over the last ten years to identify potential gaps and complement them.
- Existing models often offered oversimplified methods that overlook the fact that healthcare technologies are usually more complex than tools that address a single specific user need.
- The findings suggest an extended framework that takes into account the complexity of the healthcare ecosystem, its highly regulated nature, and interdependencies
User resistance
Understanding user adoption of technology is a complex process. Research has shown that a new tool’s acceptance is not only influenced by its technical features and reliability but also encompasses other contextual factors such as social and organizational elements that affect the users’ unique views and their decisions.
This explains why, despite the constant development of healthcare technologies, many challenges still persist. Research has shown that there are situations where users, mainly clinicians, resist mHealth tools. This is particularly relevant, bearing in mind studies, both in developed and developing countries, that showed that clinicians’ adoption is the most influential factor for a successful implementation of new health technologies.
Taking the complexity of healthcare organizations into account
Given the slow adoption of new healthcare technologies, researchers have been using a multitude of frameworks to help them get a better understanding of user acceptance and adoption of these new tools. The study looked into the frameworks used to analyze mHealth adoption in 50 peer-reviewed articles published over the last ten years to identify potential gaps and complement them.
The researchers found that many commonly used frameworks offer an oversimplified view of factors that need to be looked at in much more detail. This could be due to the fact that the majority of these frameworks were not developed within a healthcare context, and thus overlook its organizational and regulatory complexity.
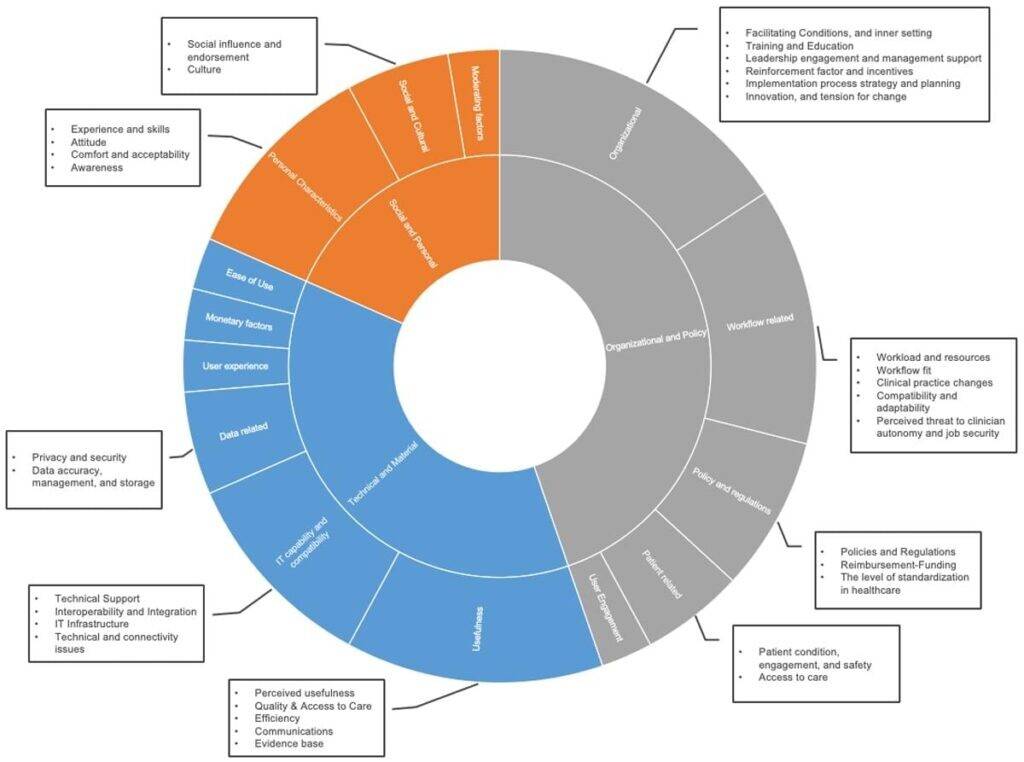
It’s important to remember that healthcare technologies are generally more complex than tools that address one specific user need. They typically serve patients with comorbidities that are mostly treated by multidisciplinary teams of clinicians, potentially working across more than one organization. This particular nature of the healthcare sector calls for some expansions to the existing technology adoption frameworks since healthcare technology cannot be successfully implemented in isolation from the broader context in which it is being used.
Looking beyond technology
The study concludes that in order to account for all relevant adoption factors fully, it is crucial to expand our focus beyond the technology itself to address clinicians’ differing concerns. These include stringent healthcare policies and regulations, data privacy and security issues, existing workload and shortage of resources, the tool’s fit into clinical practice and workflow, training and education, and leadership support.
“Our aggregated framework suggests a shift toward a more holistic view of technology acceptance in healthcare, one that does not only look into a tool’s technical features, but also takes into account the specificity of the healthcare ecosystem, and the interdependence between the technical, social and organizational factors,” says digital strategist Christine Jacob, the first author of the study, health tech researcher at Anglia Ruskin University, Cambridge, and external lecturer at the university of applied sciences Northwestern Switzerland.

